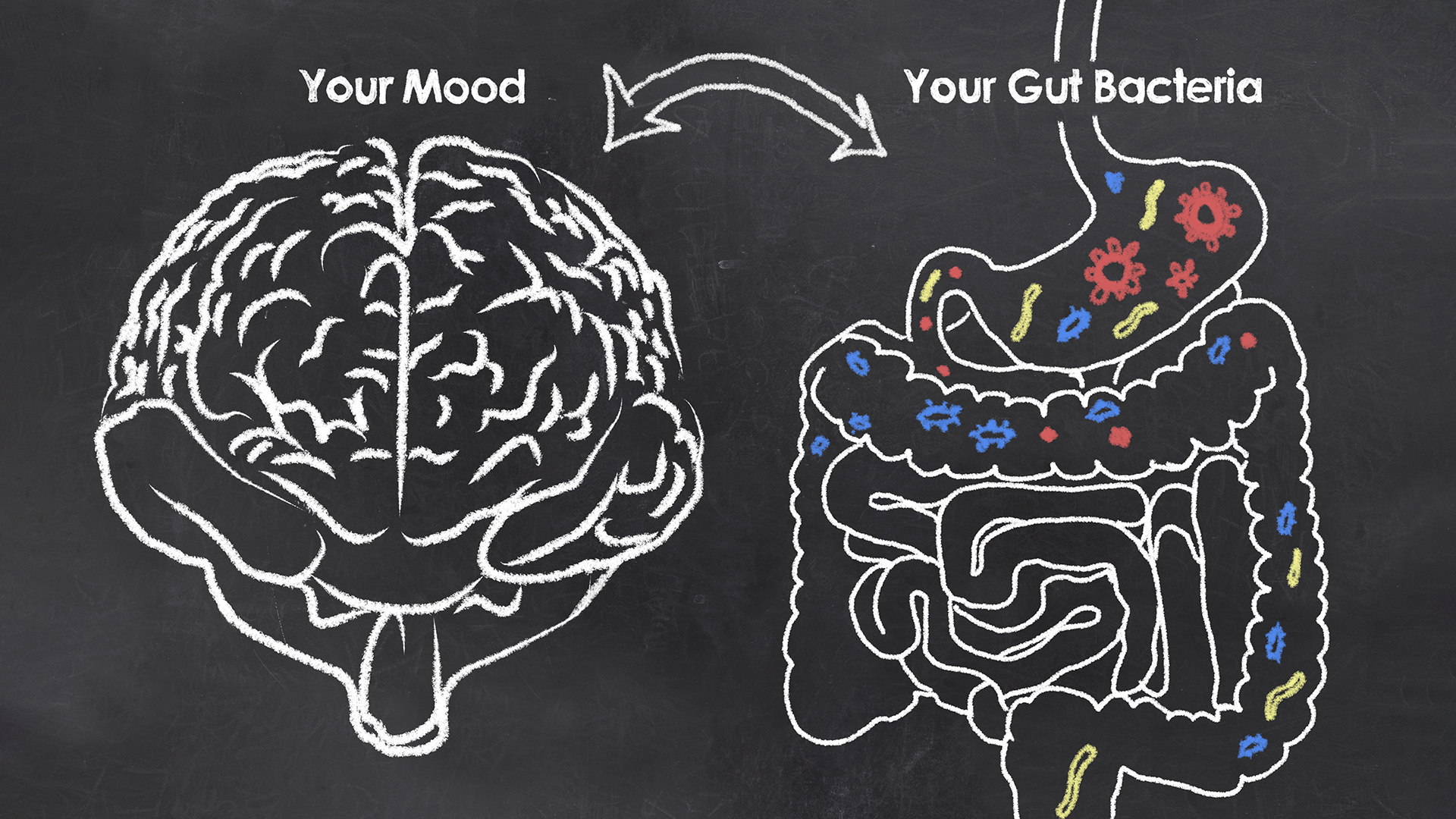
The intricate relationship between our gut and brain health is a fascinating and complex topic that warrants our attention for numerous reasons, particularly the significant impact gut health has on our mental wellness. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the science behind the gut-brain connection, including its vital role in neurotransmitter production and its effects on mental health. We will examine the links between poor gut health and common psychological issues like anxiety, depression, and cognitive debilitation.
Moreover, we will provide actionable tips on improving your gut health for optimal mental well-being, including dietary and nutrition adjustments, exercise routines tailored to enhance digestive function, and stress management techniques. Additionally, you’ll discover the benefits of essential supplements like probiotics, prebiotics, and omega-3 fatty acids to support optimal digestion and reduce inflammation.
And finally, we’ll explore the importance of seeking professional guidance from nutritionists, dietitians, and mental health professionals to ensure you’re making informed decisions regarding both aspects of wellness.
Join us as we uncover the mysteries of the gut-brain connection and discover how to optimize your physical and mental health through targeted lifestyle changes!

1. What is the Gut-Brain Connection?
The gut-brain connection refers to the complex relationship between your digestive system and your brain, which plays a crucial role in both physical and mental health. This connection is facilitated by various pathways, including hormones, immune cells, and neurotransmitters. Understanding the workings of this intricate web can help to ensure your overall health is taken care of.
Definition of the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection is a bidirectional communication system that links the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, with the enteric nervous system (ENS) found within our gastrointestinal tract. The ENS consists of millions of nerve cells that control digestion while also communicating with our CNS through various chemical messengers.
How Does the Gut-Brain Connection Work?
This fascinating link works through several mechanisms:
Vagus Nerve: The vagus nerve acts as a primary channel for transmitting signals between our gut and brain. It helps regulate essential functions such as heart rate, breathing patterns, digestion processes, mood regulation among others.
Gut Microbiota: Our intestines are home to trillions of microorganisms known collectively as gut microbiota or microbiome. These microbes play an essential role in maintaining proper digestion while also producing neuroactive compounds that influence cognitive function and emotional states.
Hormones & Immune System: Hormones like serotonin are produced in large quantities within our gastrointestinal tract; these chemicals have significant effects on mood regulation along with other vital bodily functions like appetite control. Additionally, the immune system can influence our mental health through inflammation and other immune responses that impact brain function.
The Role of Neurotransmitters in the Gut-Brain Connection
Chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters, which are responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells in the body, play an essential role in controlling a variety of physiological processes. They play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes such as mood, appetite, sleep patterns, memory formation among others. A significant portion of these neurotransmitters is produced within our gastrointestinal tract; for instance, about 90% of serotonin – often referred to as the “feel-good” hormone – is synthesized in our gut.
Research has shown that an imbalance or dysfunction in neurotransmitter production may contribute to mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. This highlights the importance of maintaining optimal gut health for overall mental well-being.

2. Common Mental Health Issues Linked to Poor Gut Health
As we mentioned above, the gut-brain connection plays a significant role in our mental well-being, and poor gut health can lead to various mental health issues. This segment will explore the psychological impacts of an unbalanced digestive system.
Anxiety and Depression
Research has shown that there is a strong link between anxiety, depression, and the state of our gut microbiome. An imbalance in the bacteria present in our digestive system can lead to inflammation and increased production of stress hormones like cortisol. This hormonal imbalance may result in symptoms of anxiety or depression.
Anxiety: Symptoms include excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, muscle tension.
Depression: Symptoms include persistent sadness or hopelessness; loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed; changes in appetite or weight; insomnia or oversleeping; fatigue;
Eating Disorders
A study published by Frontiers in Psychiatry suggests that individuals with anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder often have altered gut microbiota composition compared to healthy individuals. A study published by the Frontiers In Psychiatry journal suggests that individuals with these conditions often have altered gut microbiota composition compared to healthy individuals.
Anorexia Nervosa: Characterized by self-starvation leading to extreme weight loss, distorted body image, and an intense fear of gaining weight.
Bulimia Nervosa: Characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors such as self-induced vomiting or excessive exercise to prevent weight gain.
Binge Eating Disorder: Characterized by consuming large amounts of food in a short period without any compensatory behavior like purging or exercising excessively. This can result in obesity and other medical issues.
Cognitive Impairment and Memory Loss
Poor gut health may also affect cognitive function and memory. A study published in the journal Brain, Behavior, And Immunity demonstrated that individuals with impaired gut microbiota had reduced cognitive performance compared to those with healthy gut bacteria. Inflammation caused by an imbalanced digestive system can negatively impact brain function leading to issues such as poor concentration, forgetfulness, confusion, and even dementia in severe cases.
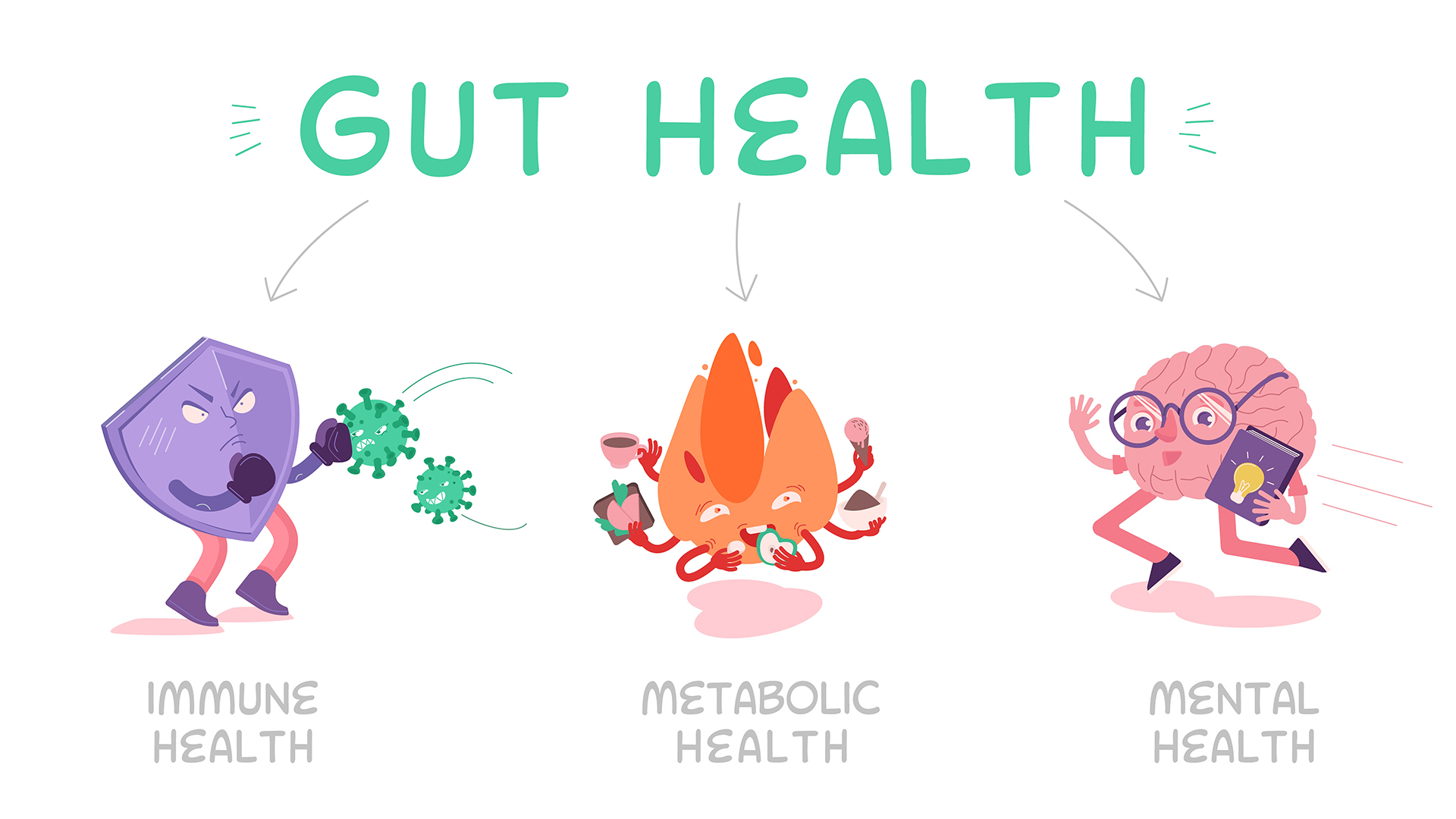
3. Improving Your Gut Health for Better Mental Health
Looking after your digestive system is critical for not only physical health but also to promote mental well-being. There are several ways to improve your gut health and consequently support better mental wellness. In this section, we will discuss diet and nutrition, exercise, and stress management as key factors in achieving optimal gut-brain connection.
Diet and Nutrition for Improved Gut Health
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in promoting good gut health. Incorporating the following foods into your daily meals can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome:
Fiber-rich foods: Consuming high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds helps promote regular bowel movements and feed beneficial bacteria in the digestive system. A great example is bananas, which are rich in fiber and prebiotics.
Fermented foods: Foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi contain probiotics that help replenish the friendly bacteria population in our guts. Learn more about fermented food benefits from this comprehensive guide on Harvard Medical School’s blog.
Lean proteins: Including lean protein sources such as fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids), poultry without skin or fat trimmed off red meat can contribute to overall digestive function improvement.
Limited processed foods: Minimizing consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and unhealthy fats can help maintain a healthy gut environment. Opt for healthier alternatives like these snack ideas designed specifically for busy moms.
Exercise for Improved Gut Health
Maintaining an active lifestyle has been shown to improve digestive health and support mental well-being. By exercising regularly, you can stimulate the muscles in your gastrointestinal tract to improve digestion and avoid constipation. Additionally, physical activity can reduce stress levels which may negatively impact gut health if left unchecked. Aim to incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activities such as brisk walking or swimming into your daily routine; even short bursts of movement throughout the day can make a difference.
Stress Management for Improved Gut Health
Managing stress is another essential aspect of maintaining good gut health since chronic stress can lead to imbalances in our gut microbiome. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation or yoga are effective ways to manage stress and promote overall mental wellness. You might also consider joining local support groups or seeking professional counseling if you find it difficult to cope with everyday challenges alone.
In addition to these practices, ensure that you get enough sleep each night—aim for 7-9 hours—as inadequate sleep has been linked with poor gut health, too.

4. Supplements to Support Mental Wellness Through Improved Gut Health
While a balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial for maintaining good gut health, certain supplements can also provide additional support for your digestive system and mental wellness. Here are some of the most effective supplements that can help improve your gut health:
Probiotics and Prebiotics for Improved Digestive Function
Probiotics are live bacteria that promote a healthy balance of gut flora, while prebiotics serve as food for these beneficial bacteria. Including both probiotics and prebiotics in your supplement regimen can help maintain optimal digestive function, which may positively impact your mental health.
Probiotic-rich foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso soup.
Prebiotic-rich foods: Garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus.
Suggested supplements: Lactobacillus acidophilus or Bifidobacterium bifidum probiotic capsules; fructooligosaccharides (FOS) or inulin prebiotic powder.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Reduced Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce inflammation in the gut, which may alleviate symptoms of poor mental health. Omega-3s are available in food sources or as supplements.
Omega-3-rich foods: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines; walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds.
Suggested supplements: Fish oil capsules or algae-based DHA+EPA supplements for vegetarians and vegans.
Herbal Supplements to Support Healthy Digestion
Certain herbs have been used traditionally to support digestive function and overall gut health. Popular herbs used to support digestion and gut health include ginger, peppermint, chamomile, and fennel seeds. These herbs can be consumed as teas or taken in supplement form to aid digestion and promote mental wellness through improved gut health.
Ginger tea: Can help soothe an upset stomach and improve digestion by increasing gastric motility (source).
Peppermint oil capsules: May relieve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) such as bloating and abdominal pain (source).
Fennel seed extract: Known for its carminative properties that help expel gas from the intestines (source).
Chamomile tea: Can help alleviate gastrointestinal discomfort and promote relaxation (source).
Combining these supplements with a balanced diet, exercise and methods to manage stress can have a major effect on gut health and mental wellbeing. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
5. Professional Help for Optimal Mental Wellness Through Improved Gut Health
While making lifestyle changes and incorporating supplements can significantly improve your gut health, sometimes it’s necessary to seek professional help to achieve optimal mental wellness through a healthy digestive system. For personalized guidance to achieve optimal mental wellness through improved gut health, consulting a nutritionist or dietitian and a mental health professional can be beneficial.
Working with a Nutritionist or Dietitian
A nutritionist or dietitian is an expert in food and nutrition who can assess your current eating habits, identify areas of improvement, and develop customized meal plans that promote better gut health. They may advise making alterations to one’s diet, like augmenting fiber intake, cutting back on processed food items, or including more fermented edibles into everyday meals. By following their advice on proper nutrition for improved gut function, you’ll be taking essential steps towards enhancing both physical and mental well-being.
Working with a Mental Health Professional
Mental health professionals like psychologists or therapists play an important role in addressing the emotional aspects of the gut-brain connection. They can help you identify potential stressors affecting your digestion while providing coping strategies for managing anxiety, depression, or other mood disorders linked to poor gut health. You might also benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on changing negative thought patterns that contribute to unhealthy behaviors impacting both mind and body.
Talk Therapy: Engaging in talk therapy sessions allows individuals to express their feelings about how their digestive issues impact daily life while receiving support from a mental health professional.
Relaxation Techniques: Learning relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and improve gut function.
Lifestyle Changes: A mental health professional may suggest incorporating regular exercise, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, or practicing self-care activities to support overall emotional well-being and gut health.
The close association between our digestive system and mental health is essential to understand, as it can have an intense effect on one’s psychological state. It’s essential that we take steps to ensure optimal gut health in order to improve and maintain positive mental well-being. Supplements may be beneficial for some people, but professional help should always be sought if needed. Taking care of your physical and mental well-being through the understanding of how your digestive system impacts your mental health is key for long term health.
Unlock the power of your gut-brain connection and take control of your mental health. Discover how to improve digestion, reduce stress, and increase overall wellbeing today!